Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

When it comes to building power, not all practices are equal. Some exercises activate more muscle groups, cause larger hormonal responses, and produce excellent functional and exercise results. These are called Compound exercises– Large-scale movements that mimic real-life patterns (such as squats, hinges, pushes and pulls).
In strength training, a few basic exercises are above the rest. These lifts have extensive research and consistently recommended for strength coaches, physical therapists and sports scientists, and are very effective in developing whole body strength, improving performance and preventing injuries.
This article outlines the five most important strength exercises that prioritize in your program and explains its benefits, appropriate forms, changes, and integration strategies based on your training goals.
Each exercise in this list is:
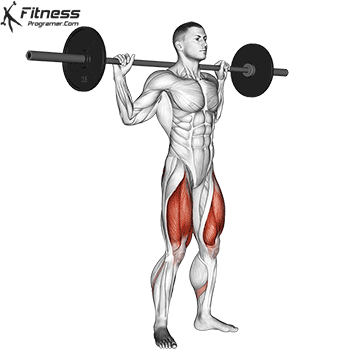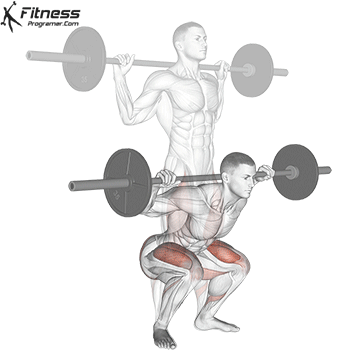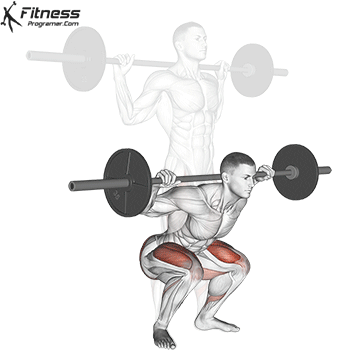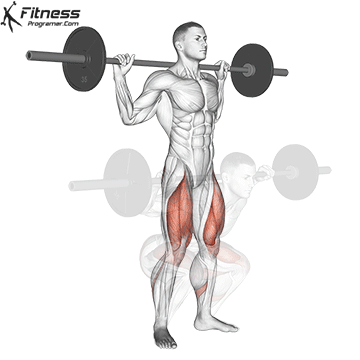
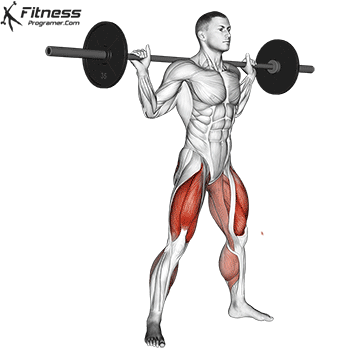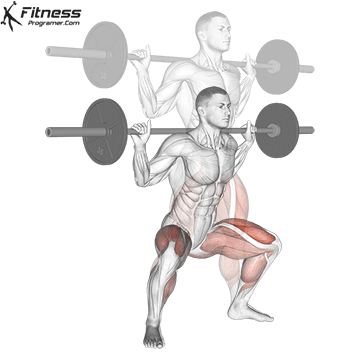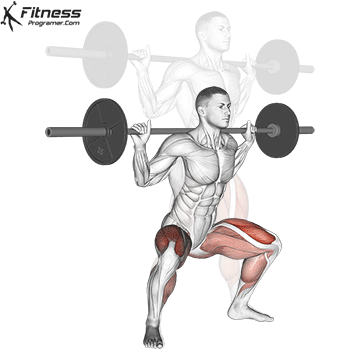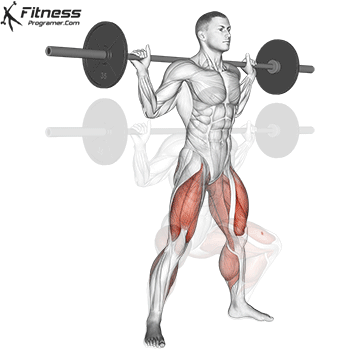
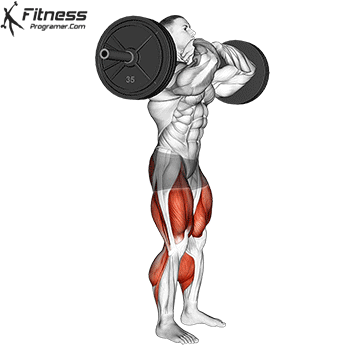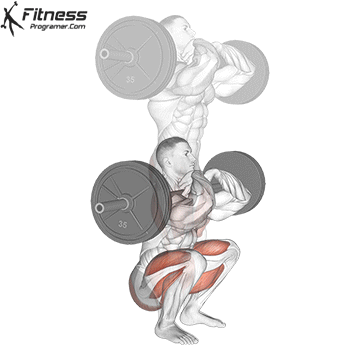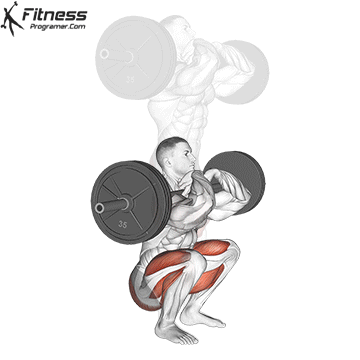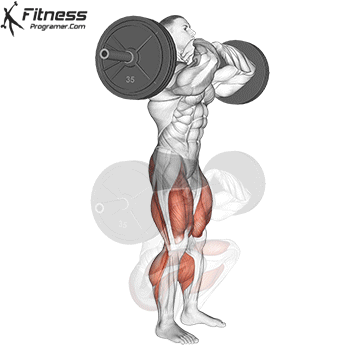
Muscles work: Quadricepships, HamstringsErectile spine
Sport mode: Lower body push dominated by knee joint
Barbell rear squat is widely considered The King of Low Lift and one of the three core exercises in weightlifting. It develops Explosive powerhypertrophy and stable posture Stimulating muscle building hormones, e.g. Testosterone and growth hormone. This lift improves athletic performance in activities such as running, jumping and lifting heavy objects from the ground.
By participating with nearly every major muscle group in the lower body and core, squats help to establish powerful and functional exercise patterns that are essential for exercise and everyday life.
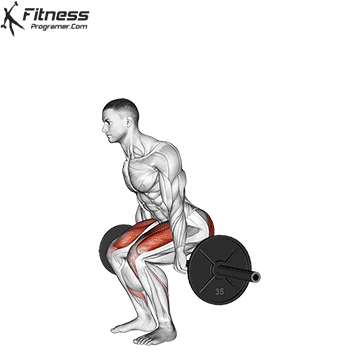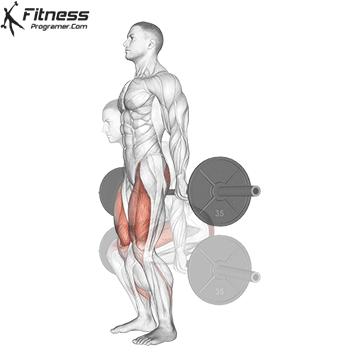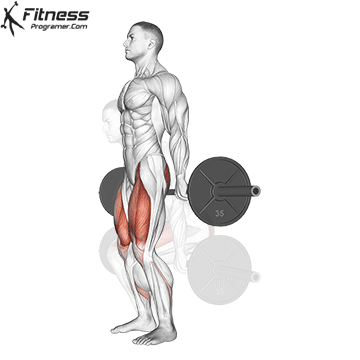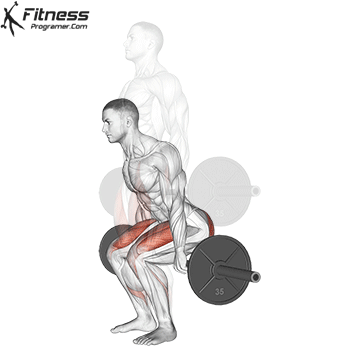
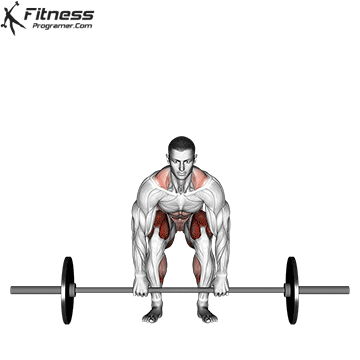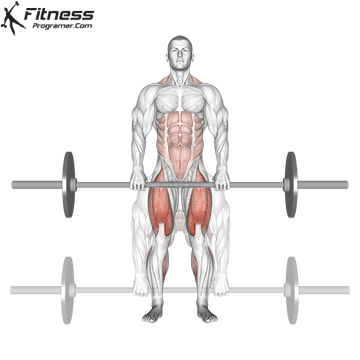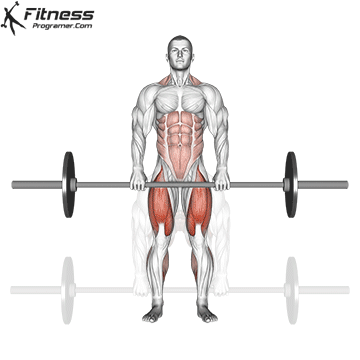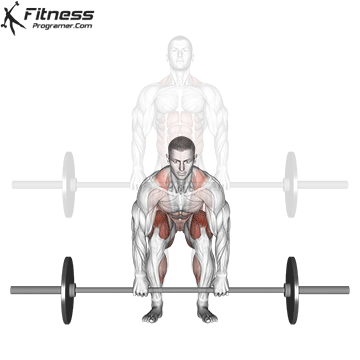
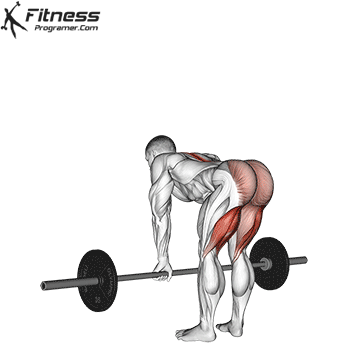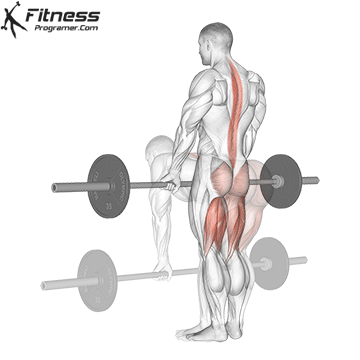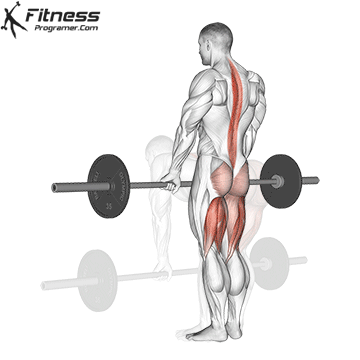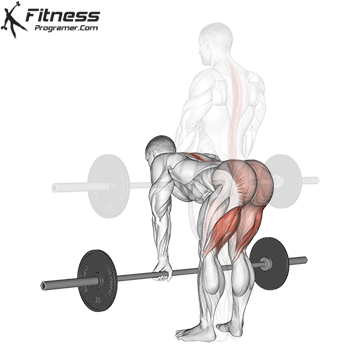
Muscles work: hips, hamstrings, erect spine, traps, lats, core
Sport mode:Hip hinge
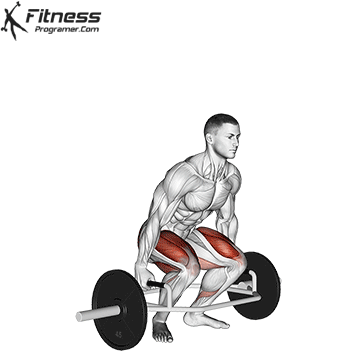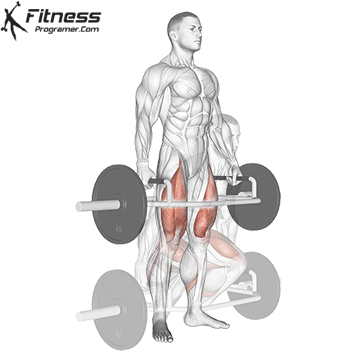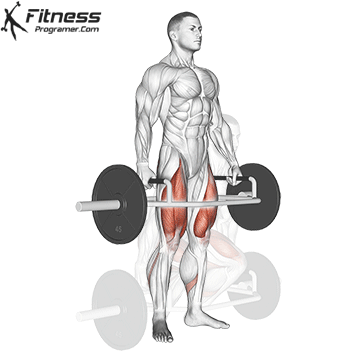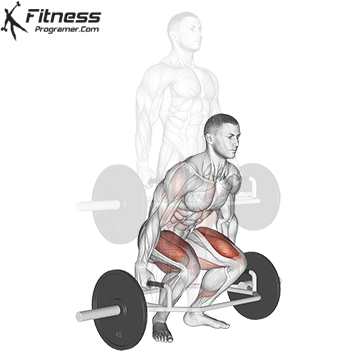
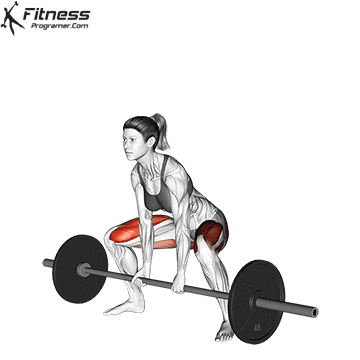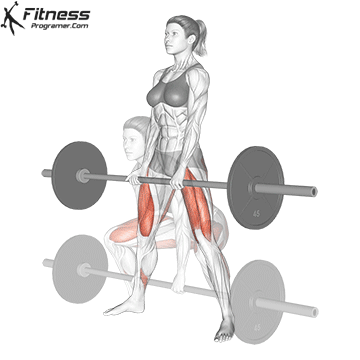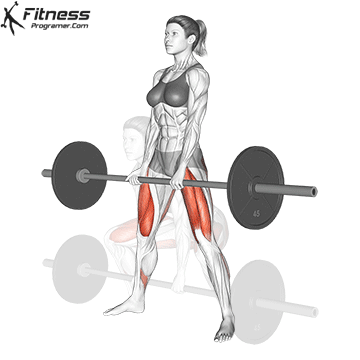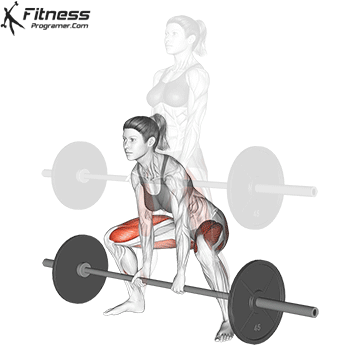
Deadlift is The cornerstone of weightliftingbench press and squat next to it. It is unparalleled development Backlink strengthwhich includes hips, hamstrings and lower back. This exercise has improved Gripcoordinate posture and overall body, while building functional abilities that can be used for daily improvement tasks and athletic performance.
Its ability to target large muscle groups at the same time also makes it highly effective for fat loss and metabolic conditions. From competitive weightlifters to general trainees, mastering deadlifts is crucial for long-term strength development.
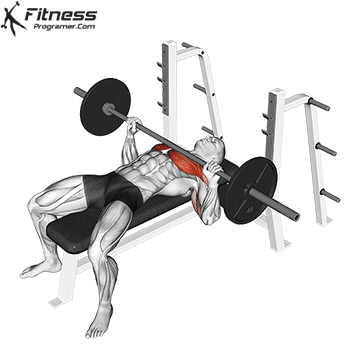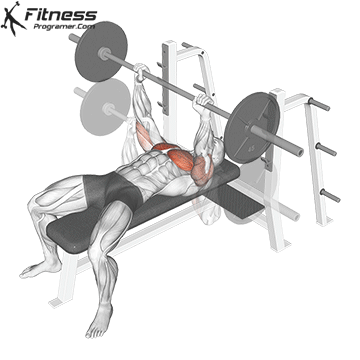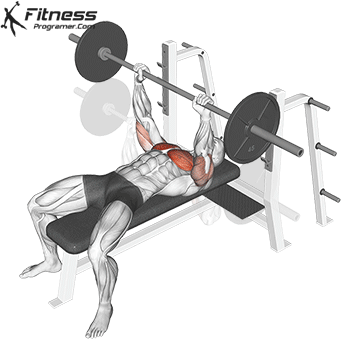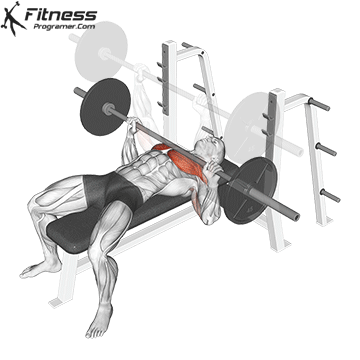
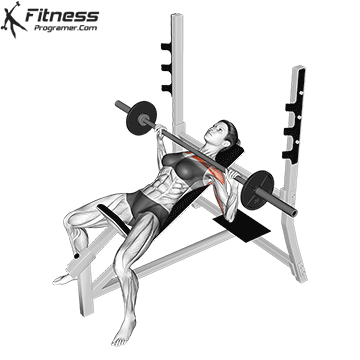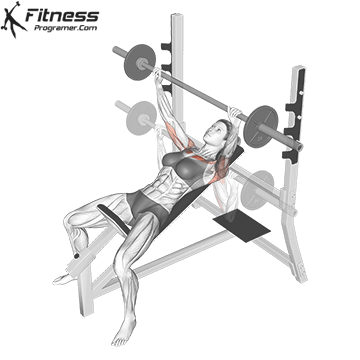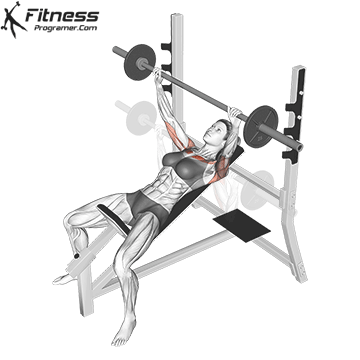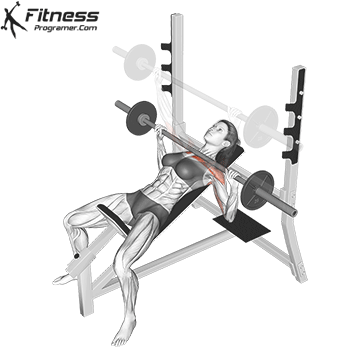
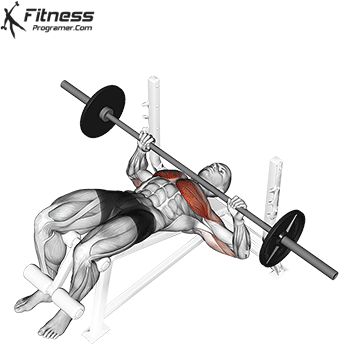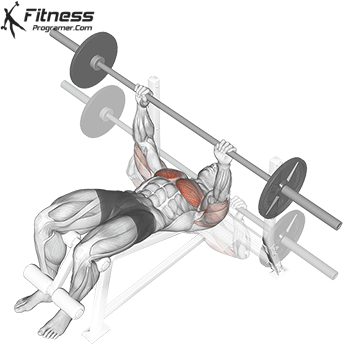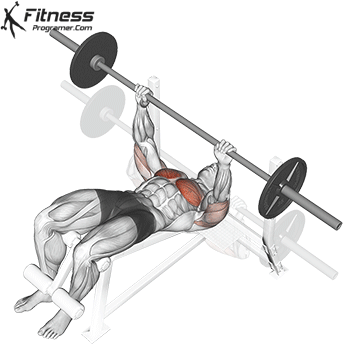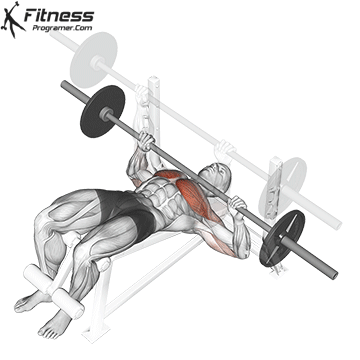
Muscles work: Chest, deltoid muscle, triceps
Sport mode: Horizontal body push
Bench press is more than Weightlifting in three gamesbut it is also a gold standard test Upper body push. It targets major muscles such as chest and triceps, Hypertrophy and the power plan. Developed bench press people support functional sports, such as pushing the door open, carrying objects and support during sports activities.
Continuous training on bench tables helps improve Muscle mass, stress mechanics, and joint stabilityespecially paired with pull exercises to ensure muscle balance.

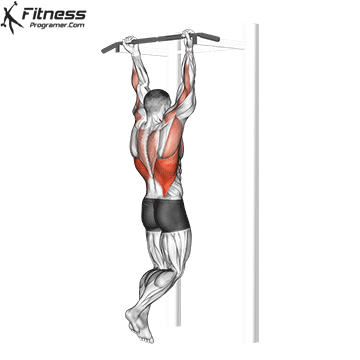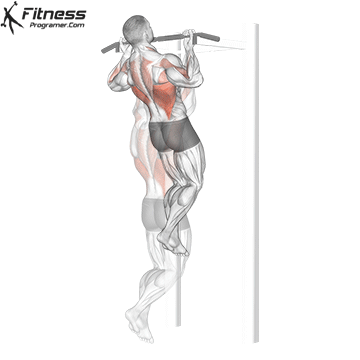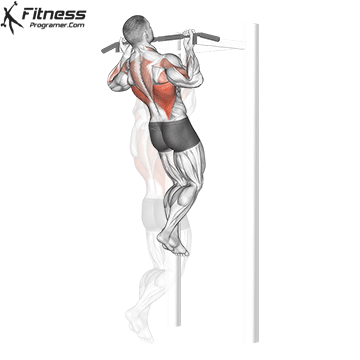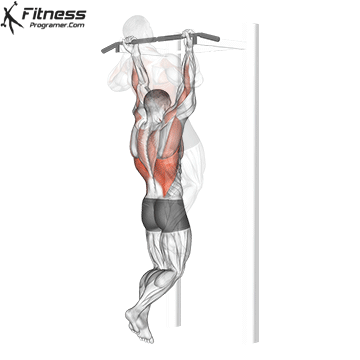
Muscles work:lats, biceps, rhombus, posterior, core
Sport mode: Pull vertically
Although not one of the traditional weightlifting competitions, pull-up is a Important companion exercises To balance the push movement found on the bench. It trains the pulling mechanism that is essential for joint health, posture and up and down strength.
Pull-up will also be built Grip and core controlmaking them a favorite among bodybuilders, Crossfit athletes and tactical professionals. In weightlifting, strong and upper back are essential for stability during squatting and deadlifting, which provides a necessary attachment exercise for strength athletes.

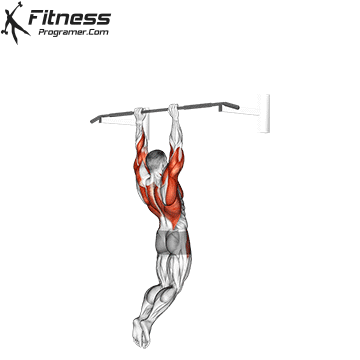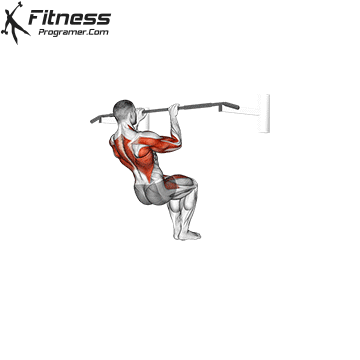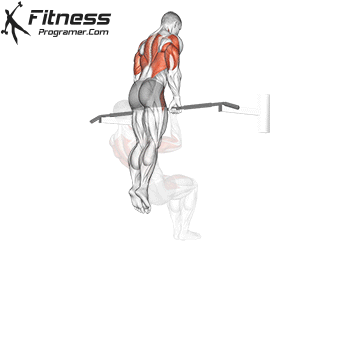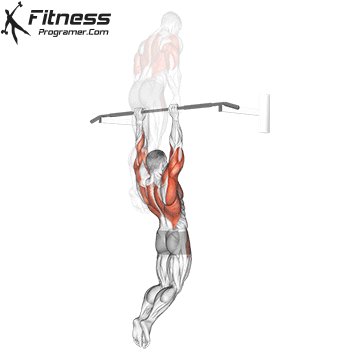
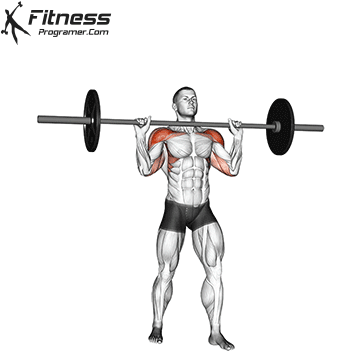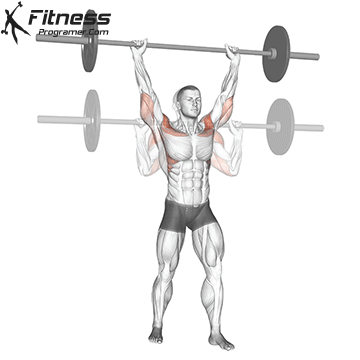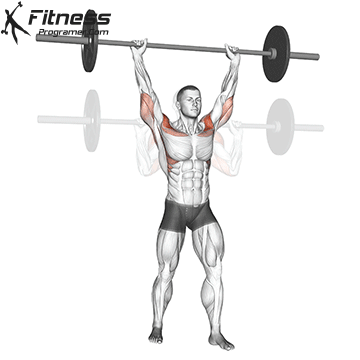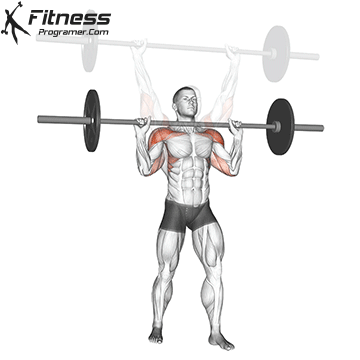
Muscles work: Deltoid muscle, triceps, traps, core
Sport mode: Vertical push
Standing upper press development Shoulder and upper back strengthwith height transfer to movement, lifting tasks and general functional movement. Although not included in competitive weightlifting, it used to be a staple Olympic lift and was often used by weightlifters to build elevated stability and pressure intensity to complement bench presses.
Press on the top of the head when standing, engaging the core, hips and legs, teaching the body to generate force while stabilizing external loads – A Key skills for sports and real-world missions.
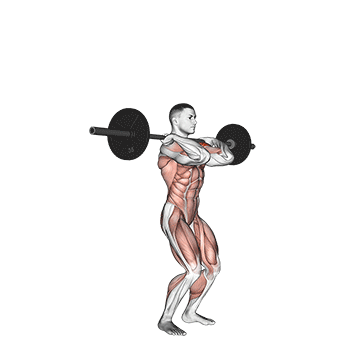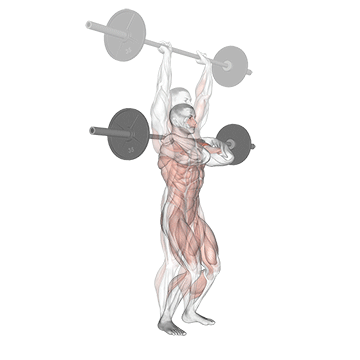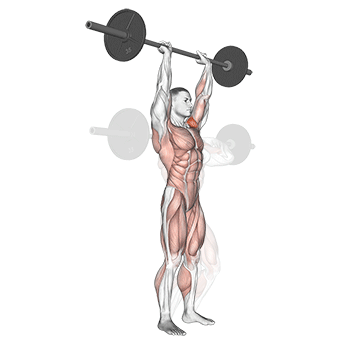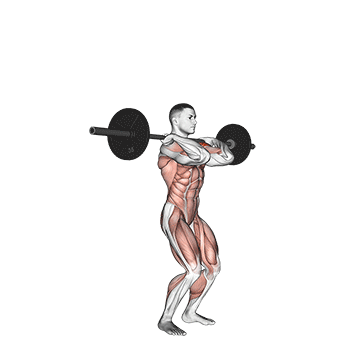
| Target | Weekly frequency | Representatives and sets | Load range |
|---|---|---|---|
| strength | 2–3x per week | 3–6 sets 3–6 times | 80–90% of 1RM |
| Hypertrophy | 4-5 times a week | 3–4 groups 8–12 times | 65–75% of 1RM |
| Fat loss | 3 times a week | Circuit format, a higher representative | 50–65% of 1RM |
| General fitness | 3 times a week | 2–3 sets 8–10 times | Moderate load |
Training Tips: Paired push and pull movements (e.g., bench press with pull) to maintain muscle balance and joint health.
Five most important strength exercises –Squat, deadlift, bench press, pull-up and overhead press– There are cornerstones in every effective training program. They offer unparalleled value Building strength, muscle, bone density, mobility and metabolic health. Mastering these sports, making smart progress and including change ensures long-term performance and prevents injuries.
refer to